学习过数据结构的小伙伴们,对单链表想来是并不陌生。本篇文章将为大家介绍几种在 Java 语言当中,实现单链表反转的几种方法,以下是具体内容。
一、原地反转
1、新建一个哨兵节点下一结点指向头结点
2、把待反转链表的下一节点插入到哨兵节点的下一节点
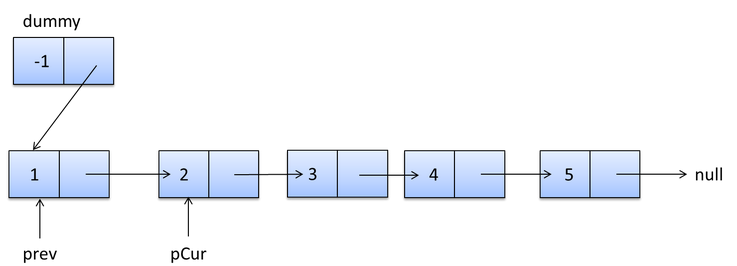
反转之前的链表:1–>2–>3–>4>–>5
加入哨兵节点:dummp–>1–>2–>3–>4>–>5
原地反转:
定义:prev=dummp.next; pcur=prev.next;
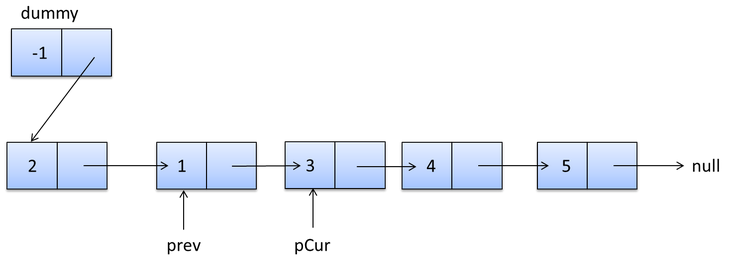
prev.next=pcur.next;
pcur.next=dummp.next;
dummp.next=pcur;
pcur=prev.next;
public Stu_node reverse_list(Stu_node head){
if (head.next==null ||head.next.next==null)
return null;
Stu_node dump = new Stu_node(-1," ");
dump.next=head;
Stu_node prev = dump.next;
Stu_node pcur = prev.next;
while(pcur!=null){
prev.next=pcur.next;
pcur.next=dump.next;
dump.next=pcur;
pcur=prev.next;
}
return dump.next;
}二、新建链表头结点插法
二、新建链表头结点插法:
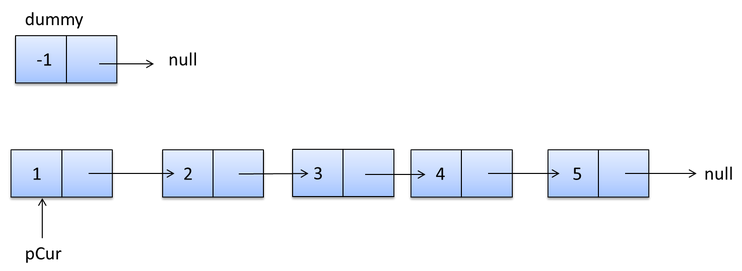
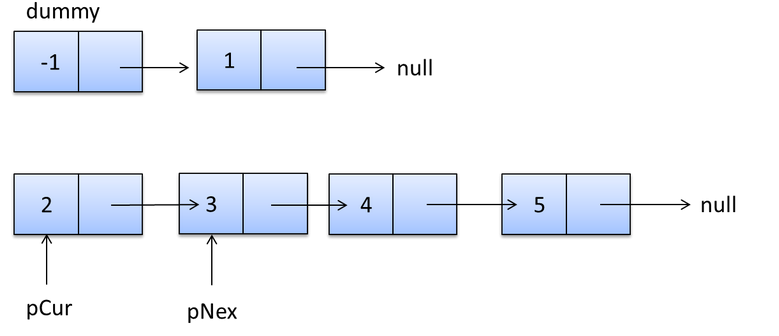
新建一个头结点,遍历原链表,把每个节点用头结点插入到新建链表中。最后,新建的链表就是反转后的链表。
public Stu_node reverse_list1 (Stu_node head){
//新建一个新的链表的头结点
Stu_node dump = new Stu_node(-1," ");
Stu_node pcur = head;
//遍历待反转链表,头结点插入到新的链表中
while(pcur!=null){
Stu_node pnext = pcur.next;
pcur.next = dump.next;
dump.next=pcur;
pcur=pnext;
}
//新链表头结点不是需要返回的数据,因此返回头结点的下一节点
return dump.next;
}三、利用栈结构实现链表的反转
由于栈结构存储数据是先进后出(后进先出)也可以通过栈达到反转链表的目的。
public Stu_node reverse_stack(Stu_node head){
Stack<Stu_node> stack = new Stack<>();
Stu_node temp = head;
//链表入栈
while(temp!=null){
stack.push(temp);
temp=temp.next;
}
//取出栈中的一个节点当做新的链表的头结点
Stu_node new_head = stack.pop();
Stu_node cur = new_head;
//出站
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
Stu_node node = stack.pop();
//将出站的节点指向取消
node.next=null;
//将新的链表串起来
cur.next = node;
cur = node;
}
return new_head;
}四、完整代码奉上
import java.util.Stack;
public class revere_node {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedNode list= new LinkedNode();
Stu_node node1 = new Stu_node(1,"张三");
Stu_node node2 = new Stu_node(2,"李四");
Stu_node node3 = new Stu_node(3,"王二");
Stu_node node4 = new Stu_node(4,"麻子");
Stu_node node5 = new Stu_node(5,"赵六");
//打印添加节点之前的链表
list.print();
//尾结点添加节点
list.add(node1);
list.add(node2);
list.add(node3);
list.add(node4);
list.add(node5);
//打印添加加点之后的链表
list.print();
System.out.println("-------------------");
//定义一个头结点接收调用函数返回的头节点
Stu_node head = list.reverse_stack(list.head);
//遍历输出每个节点
while (head.next!=null){
System.out.println(head);
head=head.next;
}
}
}
//定义一个链表的操作类
class LinkedNode{
//定义一个头结点
Stu_node head = new Stu_node(-1," ");
//添加链表的方法
public void add(Stu_node node){
Stu_node temp = head;
while(true){
if (temp.next==null)
break;
temp=temp.next;
}
temp.next=node;
}
//打印链表
public void print(){
Stu_node temp = head.next;
if (head.next==null){
System.out.println("此链表为空");
}
while (temp!=null){
System.out.println(temp);
temp=temp.next;
}
}
//原地反转
public Stu_node reverse_list(Stu_node head){
if (head.next==null ||head.next.next==null)
return null;
Stu_node dump = new Stu_node(-1," ");
dump.next=head;
Stu_node prev = dump.next;
Stu_node pcur = prev.next;
while(pcur!=null){
prev.next=pcur.next;
pcur.next=dump.next;
dump.next=pcur;
pcur=prev.next;
}
return dump.next;
}
//新建一个新的链表,头结点插入法实现链表的反转
public Stu_node reverse_list1 (Stu_node head){
Stu_node dump = new Stu_node(-1," ");
Stu_node pcur = head;
while(pcur!=null){
Stu_node pnext = pcur.next;
pcur.next = dump.next;
dump.next=pcur;
pcur=pnext;
}
return dump.next;
}
//利用栈实现反转链表
public Stu_node reverse_stack(Stu_node head){
Stack<Stu_node> stack = new Stack<>();
Stu_node temp = head;
//链表入栈
while(temp!=null){
stack.push(temp);
temp=temp.next;
}
//取出一个节点当做新的链表的头结点
Stu_node new_head = stack.pop();
Stu_node cur = new_head;
//出站
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
Stu_node node = stack.pop();
//将出站的节点指向取消
node.next=null;
//将新的链表串起来
cur.next = node;
cur = node;
}
return new_head;
}
}
//节点类
class Stu_node{
int num;
String name;
Stu_node next;
//重写toString方法,显示节点数据
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Stu_node{" +
"num=" + num +
", name='" + name + ''' +
'}';
}
public Stu_node(int num, String name) {
this.num = num;
this.name = name;
}
}总结
到此这篇关于使用 Java 如何实现单链表反转的多种方法的文章就介绍到这了,想要了解更多相关 Java 数据结构的其他内容请搜索W3Cschool以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持!


